Evidence of Common Ancestry and Diversity - Comparison of the embryological development of different species also reveals similarities that show relationships not evident in the fully-formed anatomy.
Evidence of Common Ancestry and Diversity - Comparison of the embryological development of different species also reveals similarities that show relationships not evident in the fully-formed anatomy.: Overview
This topic covers various concepts like Divergent Evolution, Analogous Organs, etc.
Important Questions on Evidence of Common Ancestry and Diversity - Comparison of the embryological development of different species also reveals similarities that show relationships not evident in the fully-formed anatomy.
Evolution in living organisms can be understood by studying the characteristics of different species. These characteristics can be different or similar based on their ancestors.
Given below are pictures of two sets P and Q, of organs of two different species. Each set is grouped based on the evolution of these organs in different species.
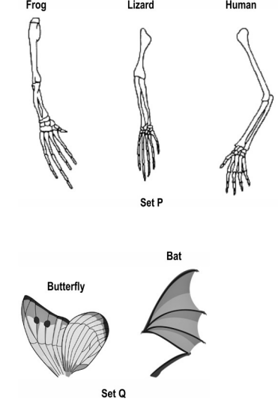
What are the differences between the two sets of organs?
Evolution in living organisms can be understood by studying the characteristics of different species. These characteristics can be different or similar based on their ancestors.
Given below are pictures of two sets P and Q, of organs of two different species. Each set is grouped based on the evolution of these organs in different species.
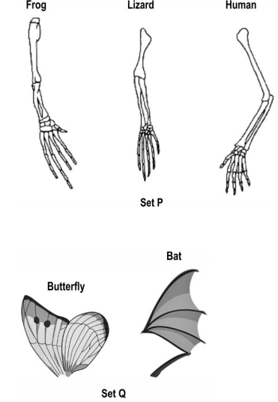
Name the scientific terms that describe the evolutionary relationship of organs in sets P and Q.
Coelacanth is a deep sea dwelling fish that was believed to be extinct 66 million years ago, around the same time the dinosaurs went extinct. However, in 1938 a specimen of the fish was discovered near the shores of South Africa. Scientists also believe that this fish may be the member of species of fish that crawled onto land to evolve into animals with legs. Upon investigation of the specimen by marine biologists certain features of the fish was discovered.
Some of them are listed below:
(i) It has paired lobe-shaped fins that move in an alternating pattern similar to the limbs of a four-legged animal. (i) It has a lung in its body but carries out exchange of gases through gills.

The lobed fin of the fish and limbs of a terrestrial animal have similar structure but different function. What are such organs called?
Select the set of analogous organs from the following:-
Among the following sets of examples for divergent evolution, select the incorrect option.
Define divergent evolution.
Give an example of convergent evolution.
What do you understand by convergent evolution?
The organs which have a similar basic structure and similar embryonic origin are called 'X' organs. 'X' features arise from adaptive behaviour, to adapt to different environmental conditions and modes of life. The organs which are quite different in fundamental structure and embryonic origin are called 'Y' organs. 'Y' feature arises when two unrelated species adapt themselves to similar climate and environmental condition.
Wings of bird, bat, insects are examples of X or Y?
Observe the following diagram and write whether these are homologous organs or analogous organs.
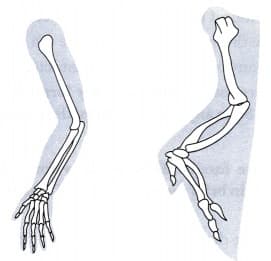
Write differences between homologous and analogous organs.
Explain the terms ‘analogous organs’ and ‘homologous organs’ with examples.
In what way are homologous organs evidence for evolution? (2)
Which one of the following mixtures will act as buffer?
Which of the following sets do not have homologous organs?
